Multiple Categorization
Status: Manuscript in preparation.
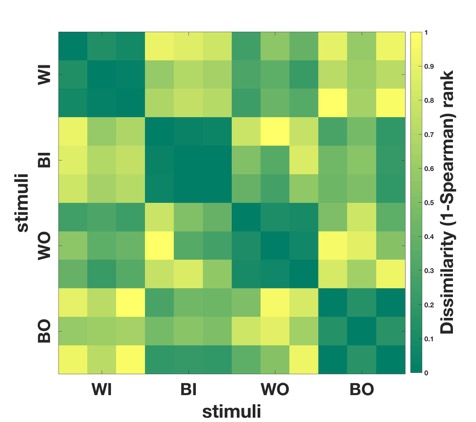
We’ve been using Representational Similarity Analysis (RSA) on EEG data to compare models of group categorization. Participants viewed videos of minimal in-group and out-group members who were also racial in-group or out-group members. Models can distinguish target race or target minmal group membership for nearly the entire video presentations. Our larger research question, however, is how multiply categorized targets are represented. Are we right to assume that double in-group members (same race, same minimal group) are most different from double out-group members (other race, other minimal group)? Which partial in-group members (same on only one dimension) are represented more similarly to double in-group members? Thus far we have not been able to differentiate models preferring race from models preferring group, but analyses are ongoing.